Lesson 2
What is cryptocurrency?
Digital money for the new global economy
A cryptocurrency is a digital asset that uses cryptography to secure and verify transactions. Cryptocurrency can be used in many of the same ways as traditional fiat currencies, such as a means for exchange or for investment purposes.
But unlike fiat currencies that are issued and controlled by central banks, most cryptocurrencies are governed in a decentralized manner by communities and blockchain protocols.
Bitcoin, the first and most well-known cryptocurrency, was created in 2009. It was soon followed by other cryptocurrencies that shared many of Bitcoin’s characteristics but also had unique features of their own.
For example, in 2011, the XRP token (built on the XRP Ledger) was created to provide a more sustainable and efficient alternative to bitcoin.
How do cryptocurrencies work with blockchains?

Cryptocurrencies are assets that exist on a blockchain. Public blockchains are decentralized and immutable ledgers that serve as a historical record of all transactions on the network. Each blockchain has its own rules, protocols and tokenomics.
If the cryptocurrency or digital asset token is a train, the blockchain protocol is the track that it’s running on. In other words, the blockchain protocol is the technological and cryptographic foundation for how digital assets are built and transactions are logged.
For example, let’s say Jane wants to send one Bitcoin to John.
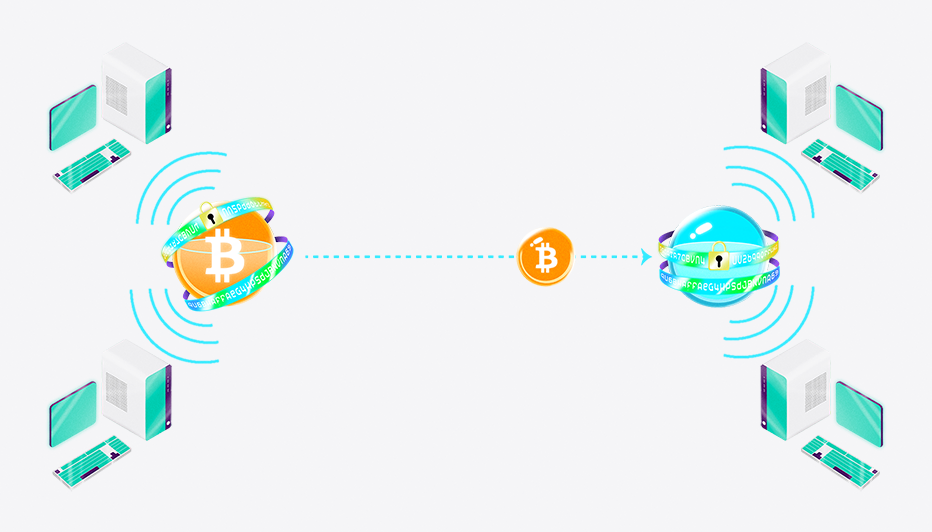
- First, she creates a transaction on the Bitcoin network that includes John’s public key (or address) and the amount of Bitcoin she wants to send him
- This transaction is then broadcast to the decentralized network of computers that power the Bitcoin network
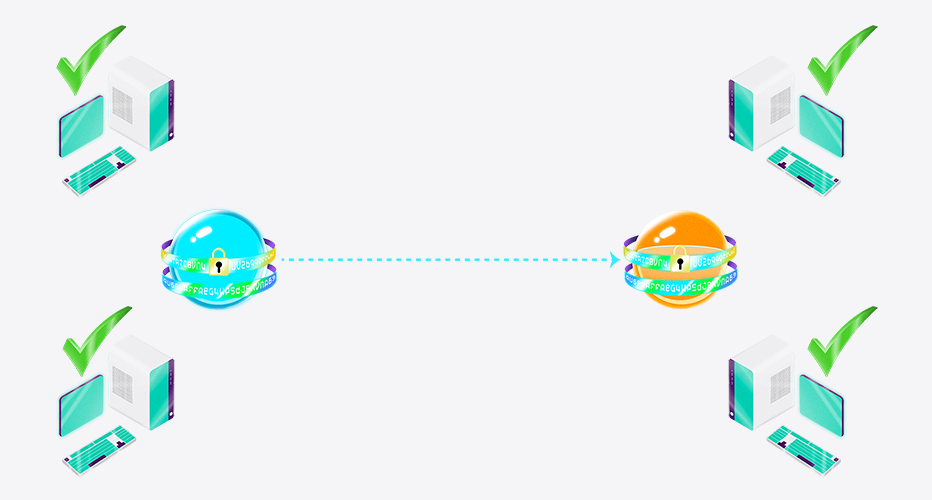
- These computers, called miners, verify the transaction by solving complex mathematical puzzles
- Once the transaction is verified, it is added as a “block” to the Bitcoin network’s blockchain and Jane’s transaction is complete.
- The entire process happens in a matter of minutes and all transactions are publicly verifiable.
This is just one example of how a cryptocurrency transaction can work with a blockchain. There are many different types of blockchains and cryptocurrencies, each with its own set of rules and protocols.
Cryptocurrencies can be kept safe using a cryptocurrency wallet. Unlike a physical wallet, your cryptocurrency doesn’t actually live inside the wallet. Instead, your wallet stores your private key, which is used to speak to the blockchain and access your cryptocurrency.
There are hardware wallets (physical devices like USB drives), software wallets (apps that live on your computer or phone), or even paper wallets (printed out keys and QR codes).
Other types of digital assets and tokens
There are many other types of digital assets/tokens that exist on their own blockchain protocols. In fact, through tokenization, almost anything can be turned into a digital asset/token.
Tokenization is the process of converting a physical asset, such as art or real estate, into a digital token that can be stored on a blockchain. Tokenization allows for the fractional ownership of assets and provides a way to seamlessly transfer the ownership of assets on a blockchain.
Let’s look at some other types of digital assets or tokens:
Non-fungible tokens (NFTs)
NFTs are tokens that represent a unique asset, such as a piece of digital art or a collectible. They are called non-fungible because each asset is unique and cannot be replaced by another identical token. For example, there can only be one Mona Lisa painting, and it’s the same with NFTs.
Security tokens (STOs)
Security tokens are digital assets that confirm ownership rights, such as equity in a company. These tokens usually give investors access to a company’s profits and can be traded on secondary markets. STOs are regulated by governments and must comply with securities laws.
Stablecoins
Stablecoins are digital assets that are pegged to a stable asset, such as the US dollar. The purpose of stablecoins is to provide a way to store value on a blockchain without the volatility that is typically associated with cryptocurrencies.
It’s vital that all stablecoins are backed by the stable asset they are pegged to. For example, a USD-backed stablecoin should have $100 worth of USD in reserve for every $100 worth of stablecoins that are in circulation.